7:44 AM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::17 Dec 2012::
Today Dr Jamal gives us some tips for final exam.
The tips are:
8 subjective question
-4 in section A (video part)
-4 in section B (animation part)
Answer any 3 Q from sect A n 3 Q from sect B
Please answer in 2 different booklet.
*The questions are:
-in Malay and English
-from: slide, discussion and article
How to answer?
-1-recall what u have learnt
-2-application
-->always relate on WHAT, WHY and HOW
Example of past year question..
1. Give 4 basic animation principles and how the principle help an animator to produce a good quality animation.
-->can draw
-->give example
2.jump cut scene/ cut away shot
GOOD LUCK!!
Today Dr Jamal gives us some tips for final exam.
The tips are:
8 subjective question
-4 in section A (video part)
-4 in section B (animation part)
Answer any 3 Q from sect A n 3 Q from sect B
Please answer in 2 different booklet.
*The questions are:
-in Malay and English
-from: slide, discussion and article
How to answer?
-1-recall what u have learnt
-2-application
-->always relate on WHAT, WHY and HOW
Example of past year question..
1. Give 4 basic animation principles and how the principle help an animator to produce a good quality animation.
-->can draw
-->give example
2.jump cut scene/ cut away shot
GOOD LUCK!!
7:45 AM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::10 Dec 2012::
After a short discussion, Dr Jamal set the date for video and animation presentation.
The date is 31 December 2012!!
*The marks will be given in group and also individually based on our scene.
So be prepare my dear friends.
-----------------------------------***----------------------------------------------
Dr Jamal demonstrate on how to animate.
*while animate, we can lock at the joint by adjusting the pivot point
for example: siku,lengan,kaki
*dont create animation in a whole timeline. It is because if anything/problem happen, it will effect the whole timeline and it is so tidious and complicate to edit.
-->So we can use movie in a movie-for example: King Klause
-----------------------------------***----------------------------------------------
Today we also learnt about STORYBOARD..
1.Why storyboard?
=easy to show the flow
2.Why storyboard is in small size?
=easy to draw
=no need to draw bigger.
3.In one sample of storyboard, there is a term footage. What is footage?
-->resource or example of different animation production
-->like reference
4. int: internal (inside environment for example: dalam rumah/ kelas)
ext: external (outside environment for example:padang bola/school)
5.we can use arrow to show the effect of zoom. For example:
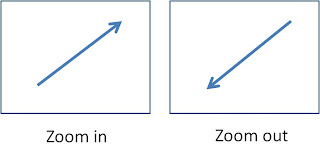
6. In storyboard we can draw a simple drawing or even using 'orang lidi' OR download image from internet.
7. Example/template of storyboard. Choose which one u want
just wanna share this video...
-animated storyboard
After a short discussion, Dr Jamal set the date for video and animation presentation.
The date is 31 December 2012!!
*The marks will be given in group and also individually based on our scene.
So be prepare my dear friends.
-----------------------------------***----------------------------------------------
Dr Jamal demonstrate on how to animate.
*while animate, we can lock at the joint by adjusting the pivot point
for example: siku,lengan,kaki
*dont create animation in a whole timeline. It is because if anything/problem happen, it will effect the whole timeline and it is so tidious and complicate to edit.
-->So we can use movie in a movie-for example: King Klause
-----------------------------------***----------------------------------------------
Today we also learnt about STORYBOARD..
1.Why storyboard?
=easy to show the flow
2.Why storyboard is in small size?
=easy to draw
=no need to draw bigger.
3.In one sample of storyboard, there is a term footage. What is footage?
-->resource or example of different animation production
-->like reference
4. int: internal (inside environment for example: dalam rumah/ kelas)
ext: external (outside environment for example:padang bola/school)
5.we can use arrow to show the effect of zoom. For example:

6. In storyboard we can draw a simple drawing or even using 'orang lidi' OR download image from internet.
7. Example/template of storyboard. Choose which one u want
just wanna share this video...
-animated storyboard
2:39 AM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::03 December 2012::
3. I also learnt new techniques today:
-fade in
-fade out
-dissolve
3. I also learnt new techniques today:
-fade in
-fade out
-dissolve
FADE IN
- at frame 1 make the box color as alpha=100%
- at frame 15, make the box color as alpha=0%
-right click at any frame 1-15 at box layer-->create motion tween
so the result will be like this:
sini
FADE OUT
- the box at frame 15 make it color as alpha=0%
-right click at any frame 15-50 at box layer-->create motion tween
so the result will be like this:
7:46 AM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::03 Dec 2012::
1. Animatic is
1. Animatic is
- like a dynamic storyboard
- a series of still images
- give idea of flow of the storyline.
These videos are the example of animatic
2. Importing image
Today i also learnt about import to stage vs import to library..
Today i also learnt about import to stage vs import to library..
what is the differences?
-->The "Import to Stage" will add the image in the Library and places a copy on the Stage, while the "Import to Library" will add the image in the Library only.
-->When you import or paste an image onto the stage, Flash stores a copy in the Library panel.
Importing image
File -> Import, then choose Import to Stage (or Import to Library).
If the graphics files have sequential names like img_02.jpg, img_03.jpg, img_04.jpg, and so on, Flash will detect the sequential files and can import the entire series (each picture in a Frame).
In this case, Flash recognises the sequential names and display a dialog box to asks if you want to import the entire series.
In this case, Flash recognises the sequential names and display a dialog box to asks if you want to import the entire series.
Reminder:
- You can drag and use from the Library on the stage multiple copies of an image.
- If you delete an image on the Stage, it still remains in the Library, but when you delete an image from Library, all of its copies will be deleted.
- Adding graphic files in Flash it increments considerably the size of the Flash file (the SWF presentation).
credit to http://coursesweb.net/flash/importing-images
3. to b continued
7:51 AM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::26 Nov 2012::
There is no class today because Dr Jamal have a workshop at faculty...
There is no class today because Dr Jamal have a workshop at faculty...
3:27 PM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::19 Nov 2012::
Today we've learnt about the principles of animation. Some of my friends presented n shared their topic (that we have to choose b4 this). After that, Dr Jamal discussed the principles with details..
Some of the principles of animation that have been highlighted:
1. SQUASH AND STRETCH
This action gives the illusion of weight and volume to a character as it moves. Also squash and stretch is useful in animating dialogue and doing facial expressions.
2.SLOW-OUT AND SLOW-IN
As action starts, we have more drawings near the starting pose, one or two in the middle, and more drawings near the next pose. Fewer drawings make the action faster and more drawings make the action slower. Slow-ins and slow-outs soften the action, making it more life-like. Or Ease in Ease Out
3. EXAGGERATION
Exaggeration is an effect especially useful for animation, as perfect imitation of reality can look static and dull in cartoons.The level of exaggeration depends on whether one seeks realism or a particular style, like a caricature or the style of an artist.pendek kate kita panggil dia 'over'
4. FOLLOW THROUGH AND OVERLAPPING ACTION
Follow through and overlapping action is a general heading for two closely related techniques which help to render movement more realistically, and help to give the impression that characters follow the laws of physics. "Follow through" means that separate parts of a body will continue moving after the character has stopped. "Overlapping action" is the tendency for parts of the body to move at different rates (an arm will move on different timing of the head and so on).
Other principles:
-Anticipation
-Staging
-Straight ahead action and pose to pose
-Arcs
-Secondary action
-Timing
-Solid drawing
-Appeal
Dr Jamal also gave us time to try to do the principle of squash n stretch using flash.
This is a video from youtube..Explaining about the principles
Today we've learnt about the principles of animation. Some of my friends presented n shared their topic (that we have to choose b4 this). After that, Dr Jamal discussed the principles with details..
Some of the principles of animation that have been highlighted:
1. SQUASH AND STRETCH
This action gives the illusion of weight and volume to a character as it moves. Also squash and stretch is useful in animating dialogue and doing facial expressions.
2.SLOW-OUT AND SLOW-IN
As action starts, we have more drawings near the starting pose, one or two in the middle, and more drawings near the next pose. Fewer drawings make the action faster and more drawings make the action slower. Slow-ins and slow-outs soften the action, making it more life-like. Or Ease in Ease Out
3. EXAGGERATION
Exaggeration is an effect especially useful for animation, as perfect imitation of reality can look static and dull in cartoons.The level of exaggeration depends on whether one seeks realism or a particular style, like a caricature or the style of an artist.pendek kate kita panggil dia 'over'
4. FOLLOW THROUGH AND OVERLAPPING ACTION
Follow through and overlapping action is a general heading for two closely related techniques which help to render movement more realistically, and help to give the impression that characters follow the laws of physics. "Follow through" means that separate parts of a body will continue moving after the character has stopped. "Overlapping action" is the tendency for parts of the body to move at different rates (an arm will move on different timing of the head and so on).
Other principles:
-Anticipation
-Staging
-Straight ahead action and pose to pose
-Arcs
-Secondary action
-Timing
-Solid drawing
-Appeal
Dr Jamal also gave us time to try to do the principle of squash n stretch using flash.
This is a video from youtube..Explaining about the principles
10:09 PM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
I've choose Secondary action for my task.
What is secondary action?
other examples:
What is secondary action?
- It is not a main movement. Just a small action.
- This action adds to the main action, adding more dimension to the character.
- Important in heightening interest and adding a realistic complexity to the animation
- Adding secondary actions to the main action gives a scene more life, and can help to support the main action.
- The important thing about secondary actions is that they emphasize, rather than take attention away from the main action.
- Example:A person walking can simultaneously swing his arms or keep them in his pockets, he can speak or whistle, or he can express emotions through facial expressions.
The character is walking across the screen, the secondary action shown here is the exaggerated swinging of the arms. This is not necessary to the character walking but it adds depth and personality to the character and the action.
This dog's collar bounces around on its neck as it walks. The collar is not the primary motion of walking, but its secondary action adds realism to the scene.
other examples:
3:28 PM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::10-18 Nov 2012::
p/s: Dont forget this task:
-find about Principles of Animation.
-Choose 1
-Find the example on how to use the principle
-Prepare not more than 5 slides
-How to use the principle in order to produce a good animation.
-will be discuss after the break!!
p/s: Dont forget this task:
-find about Principles of Animation.
-Choose 1
-Find the example on how to use the principle
-Prepare not more than 5 slides
-How to use the principle in order to produce a good animation.
-will be discuss after the break!!
3:31 PM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::5 Nov 2012::
Today is our first animation class with Dr Jamal..
We need to recall back our knowledge/skill in authoring system class or CD-rom class.
1) Keyframe :starting and ending points in animation. Should have at least 2 keyframe.
2) Tweening : derived from "in between". There are 2 type of tweening: motion tweening & shape tween
3) Onion skinning : is using for tracing picture. The tracing process will be easier especially for those "tangan keras"
4) Frame by frame : more realistic because we control everything. and the movement are more realistic.
5) Frame rate : 12-15fps is enough for animation. 15 fps is better because it need more pictures. And of course more pictures means more realistic. then more pictures means the file size will increase.
taking from http://animation.about.com/od/faqs/f/faq_fpsnumber.htm
Question: How many frames are in one second of animation?
There are 8-frame walk cycles, 10-frame motion studies...but how many frames actually make up one second of animation?
Answer: That actually depends on your method of publication and the quality you want. For standard quality web animation, there are 12 frames per second; high quality web animation downloaded over high bandwidth goes up to 15 frames per second - which is, coincidentally, the default frame rate for standard quality television animation. 24 frames per second can be either high quality TV animation, or low quality cinematic animation, while high quality cinematic animation is generally 30 fps.
So really, there is no universal "default" - but there are several standards.
Task for next class!!
-choose 1 principle of animation
-find the info
-find the example how to use the principle so that can produce a good animation
-prepare 5 slides
ingat!!!!
Today is our first animation class with Dr Jamal..
We need to recall back our knowledge/skill in authoring system class or CD-rom class.
1) Keyframe :starting and ending points in animation. Should have at least 2 keyframe.
2) Tweening : derived from "in between". There are 2 type of tweening: motion tweening & shape tween
3) Onion skinning : is using for tracing picture. The tracing process will be easier especially for those "tangan keras"
4) Frame by frame : more realistic because we control everything. and the movement are more realistic.
5) Frame rate : 12-15fps is enough for animation. 15 fps is better because it need more pictures. And of course more pictures means more realistic. then more pictures means the file size will increase.
Question: How many frames are in one second of animation?
There are 8-frame walk cycles, 10-frame motion studies...but how many frames actually make up one second of animation?
Answer: That actually depends on your method of publication and the quality you want. For standard quality web animation, there are 12 frames per second; high quality web animation downloaded over high bandwidth goes up to 15 frames per second - which is, coincidentally, the default frame rate for standard quality television animation. 24 frames per second can be either high quality TV animation, or low quality cinematic animation, while high quality cinematic animation is generally 30 fps.
So really, there is no universal "default" - but there are several standards.
Task for next class!!
-choose 1 principle of animation
-find the info
-find the example how to use the principle so that can produce a good animation
-prepare 5 slides
ingat!!!!
6:17 AM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::29 October 2012::
Continued with editing again..
Some new things learnt today:
Continued with editing again..
Some new things learnt today:
- Video Leader:opening part in video to introduce the story.
- Montage : To attract the audience.
- Non Linear editing : editing menggunakan peralatan teknologi terkini
- Linear editing : jarang/tidak digunakan lagi pada masa kini
- Loose Vs Tight editing : Loose = details Tight = not details
- Online Vs Offline editing : Offline = rough editing.
- Mark in Vs Mark out : cut in , cut out
- Assemble Vs Insert editing
3:32 PM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::22 Oct 2012::
Venue: @ Video Lab
Some shortcut can use in editing :
ctrl + r = redo
ctrl + z = undo
ctrl + x = delete
Venue: @ Video Lab
Today we learn about video editing.. En Aziz from video lab has taught us how to edit a video.
what is the purpose of editing?
-to arrange the video
-give meaning to the content
-proper sequence
Software using for editing is AvidXpress Pro.
Some tool in this software:
Title tool=add text
effect editor=preview effect that we choose
mark in
mark out
new video track= add new video.
Some shortcut can use in editing :
ctrl + r = redo
ctrl + z = undo
ctrl + x = delete
and can save in .mov and .avi
3:33 PM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::15 Oct 2012::
Today is the most valuable experience in UTM hehe...Im very excited to go to class today because we will watching live shooting for UTM convocation rehearsal...Our class today is at control room @ DSI..
Even today was very heavy rain, but we are eager to attend this class...
Today, the students make rehearsal for their convocation. .
We learn many new things today..The equipment also very expensive...almost hunderd thousand wow.......En Johari explained about function of the equipment like MCP camera, switcher and converter
MCP (Multi Camera Production)
-is a process of video production system to use more than one camera.
-take from various angles
switcher
-function: to select the signal from the camera.
-There are also video switcher that can produce some 'effect' for interesting pictures.
2:43 AM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::8 October 2012::
Some more info about lighting today...
There are 3-Point Lighting:
Key Light - Fill Light - Back Light
The best lighting technique is 3-point lighting. In 3-point lighting 3 lights are used. A key light, a fill light, and a back light.
Key light
Some more info about lighting today...
There are 3-Point Lighting:
Key Light - Fill Light - Back Light
The best lighting technique is 3-point lighting. In 3-point lighting 3 lights are used. A key light, a fill light, and a back light.
Key light
- the main light that is placed at a thirty to forty-five degree angle in front of the subject and to the side of the camera.
- is placed on the side of the camera just opposite of the key light.
- is used to soften shadows created by the key light.
- is set to about half the intensity of the key light, and often a broad, scoop, or soft light is used instead of a spotlight to provide a softer fill with no harsh shadows. If using only a 2-light system, a reflector can be used to bounce light back onto the subject. Reflectors are sometimes used with a fill light to ensure that no hard shadows are cast on the subject
- usually placed directly behind the subject, in line with the camera.
- is sometimes placed above the subject pointing down onto the head and neck of the subject.
- creates a "defining edge" to help visually separate the subject from the background, and should be adjusted so it creates a highlight around the top or side of the subject.
- is not a background light. It should not be used to light the back drop, it is only used to create a rim of light around the subject and is used to separate the subject from the background by giving it a 3-dimensional look.
Accent
- is optional
- to make the subject to come out/get away from the background/back
- the subject become 3D effect
2:44 AM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
A cutaway is a shot that's usually of something other than the current action. It could be a different subject (eg. this cat when the main subject is its owner), a close up of a different part of the subject (eg. the subject's hands), or just about anything else.
The cutaway is used as a "buffer" between shots (to help the editing process), or to add interest/information.
The cutaway is used as a "buffer" between shots (to help the editing process), or to add interest/information.
2:32 AM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::1 October 2012::
White balance (WB) is the process of removing unrealistic color casts, so that objects which appear white in person are rendered white in your photo. Proper camera white balance has to take into account the "color temperature" of a light source, which refers to the relative warmth or coolness of white light.
Our eyes are very good at judging what is white under different light sources, but digital cameras often have great difficulty with auto white balance (AWB) — and can create unsightly blue, orange, or even green color casts. Understanding digital white balance can help you avoid these color casts, thereby improving your photos under a wider range of lighting conditions.
White balance (WB) is the process of removing unrealistic color casts, so that objects which appear white in person are rendered white in your photo. Proper camera white balance has to take into account the "color temperature" of a light source, which refers to the relative warmth or coolness of white light.
Our eyes are very good at judging what is white under different light sources, but digital cameras often have great difficulty with auto white balance (AWB) — and can create unsightly blue, orange, or even green color casts. Understanding digital white balance can help you avoid these color casts, thereby improving your photos under a wider range of lighting conditions.
 |
| Color Cast |
|
|
2:07 AM -
Posted by Diyana Aziz -
0
comments
::24 September 2012::
Today I learnt many new things about video world. This is also one of my reasons for taking this class. Yes, to learn new things. And that is why most of the time in this class, I just keep quiet hehe.
En Johari also exposed to us about shot and their types. You know I
just knew that shot have so many type/size…. I only know close up hehe..
Yes it was a little bit hard for me to differentiate the type….but luckily my beloved lecturer, En Johari show shot’s size one by one, and how they were different to each other.
Here some video for better understanding.....check it out!!
Today I learnt many new things about video world. This is also one of my reasons for taking this class. Yes, to learn new things. And that is why most of the time in this class, I just keep quiet hehe.
En Johari explained to us general things about broadcasting. There are 3 major system of broadcasting:
-PAL
-NTSC
-SECAM
There are three standards of broadcasting used around the world. Most of Europe, Africa, Australia, and parts of Asia and South America use PAL. Russia and parts of Asia and Africa use SECAM. The United States, Canada, most of North and South America, and Japan use NTSC. Video devices and televisions made in countries using different standards are not compatible with one another; however, it is possible to convert signals from one broadcasting standard to another through the use of a SECAM/NTSC/PAL converter.
Read more: How to Convert PAL & SECAM to NTSC | eHow.com http://www.ehow.com/how_5458570_convert-pal-secam-ntsc.html#ixzz29GOWq1TV
 |
Yes it was a little bit hard for me to differentiate the type….but luckily my beloved lecturer, En Johari show shot’s size one by one, and how they were different to each other.
Here some video for better understanding.....check it out!!
En Jo also mentioned about pre-production, production and
post production.
Pre-production
Production
Post -production
-
I've choose Secondary action for my task. What is secondary action? It is not a main movement. Just a small action. This act...
-
::10 Dec 2012:: After a short discussion, Dr Jamal set the date for video and animation presentation. The date is 31 December 2012!! *T...
-
::24 September 2012:: Today I learnt many new things about video world. This is also one of my reasons for taking this class. Yes, to lea...
-
::19 Nov 2012:: Today we've learnt about the principles of animation. Some of my friends presented n shared their topic (that we hav...
-
Task during class: panning and zooming dissolve
-
::5 Nov 2012:: Today is our first animation class with Dr Jamal.. We need to recall back our knowledge/skill in authoring system ...
-
::22 Oct 2012:: Venue: @ Video Lab Today we learn about video editing.. En Aziz from video lab has taught us how to edit a vide...
-
A cutaway is a shot that's usually of something other than the current action. It could be a different subject (eg. this cat when the ma...
-
::17 Dec 2012:: Today Dr Jamal gives us some tips for final exam. The tips are: 8 subjective question -4 in section A (video part) -...
Assalamualaikum
About Me
Popular Posts
Powered by Blogger.
Theme by Function
© 2008 . Bloggerized by Falcon Hive.com